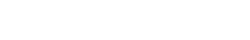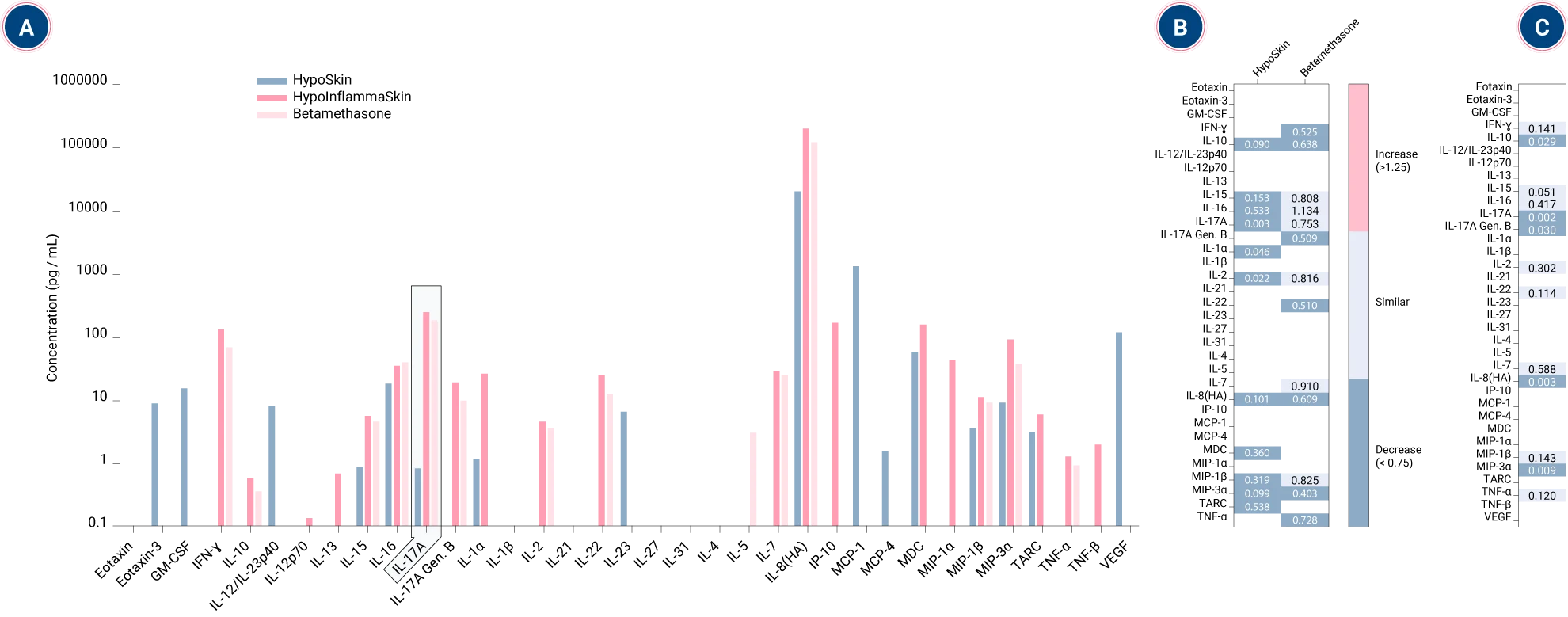Preclinical anti-psoriasis efficacy studies
Innovative anti-psoriasis drug assays for better drug development

InflammaSkin® is a human ex vivo skin model designed to replicate the early, immune-driven phases of psoriasis with high physiological relevance. Unlike reconstructed skin models or ex vivo systems that rely solely on cytokine cocktails, InflammaSkin activates resident T cells in situ prior to culture, followed by continuous cytokine stimulation to drive a robust Th1/Th17 inflammatory phenotype within native human skin. This dual-activation approach closely mimics in vivo immune dynamics, enabling drug developers to evaluate the initiation of psoriatic inflammation and assess the efficacy of both biologics and small molecules.
Reproducible
Genoskin’s human skin models are standardized for consistent, immune-relevant inflammation readouts.
T-cell driven
Our anti-psoriasis studies are based on the live response of our unique T-cell driven human psoriasis skin model.
Efficacy
We study efficacy for both biologics and small-molecule drugs and for different administration routes.
Platform
We provide immune profiling services to evaluate therapeutic and prophylactic responses in human skin models
Psoriasis, a condition with no cure
Finding new ways to help science move forward
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated skin disease that affects some 125 million people worldwide according to the World Psoriasis Day consortium. The condition has a big impact on patients who are also at risk of experiencing a range of associated diseases, such as metabolic syndrome, stroke, heart attack, cardiovascular disease and depression. About 40% of patients with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis. To date, anti-psoriasis drugs don’t provide a cure, even though biologics have helped improve symptoms. Here at Genoskin, we aim to provide drug developers with innovative solutions to help them better serve patients.
A versatile platform for testing diverse psoriasis treatment modalities
Immune-driven readouts to support early-stage & confirmatory studies

InflammaSkin® enables the assessment of a broad spectrum of psoriasis therapies, including both biologics and small molecules. Compounds can be applied topically, added to the culture medium to mimic systemic exposure, or injected subcutaneously or intradermally to reproduce clinical delivery routes. Its immune-driven response yields meaningful cell- and tissue-level readouts that support both early discovery and preclinical validation of therapeutic mechanisms.

Characterizing T cell–mediated immune dynamics with InflammaSkin®
Multi-parametric readouts reveal cytokine profiles, therapeutic response, and immune cell shifts

InflammaSkin® captures cytokine shifts in response to anti-inflammatory treatment
A.B. All cytokines for the HypoSkin control are down-regulated in comparison to the Hypo-InflammaSkin control → there is significant inflammation induction in the Hypo-InflammaSkin models at day 7.
Additionally, we observe a 300 fold increase for IL-17 between HypoSkin and Hypo-InflammaSkin, proof of the right induction in the model.
Betamethasone treatment decreased the secretion of many cytokines compared to the untreated Hypo-InflammaSkin controls, including IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-17A Gen. B, IL-22, IL-8(HA), MIP-3α, and TNF-α.
Subcutaneous administration of anti-TNFα drives dose-dependent cytokine suppression in InflammaSkin®
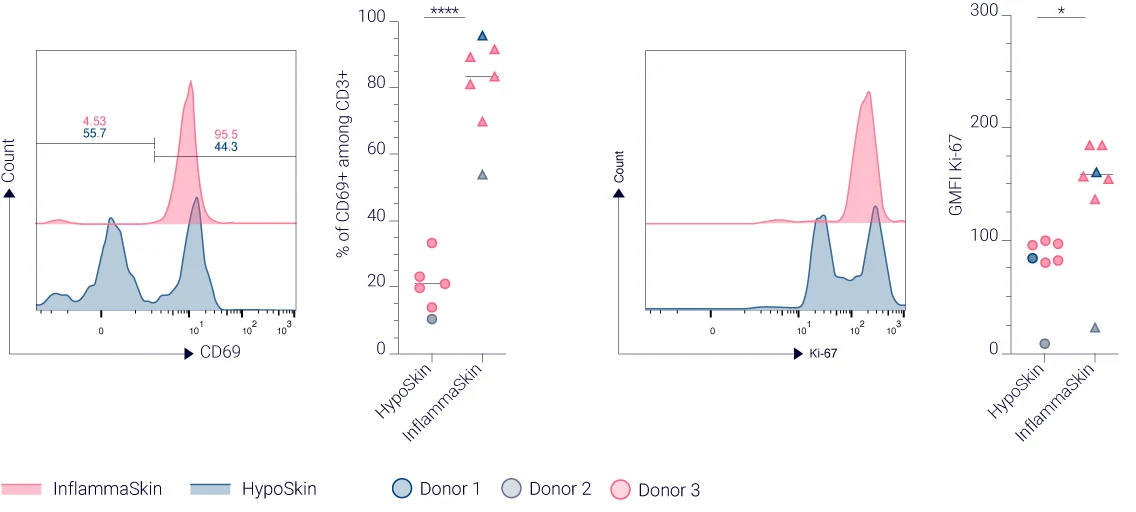
CD69 and Ki-67 expression highlights enhanced T cell activation and proliferation in InflammaSkin®
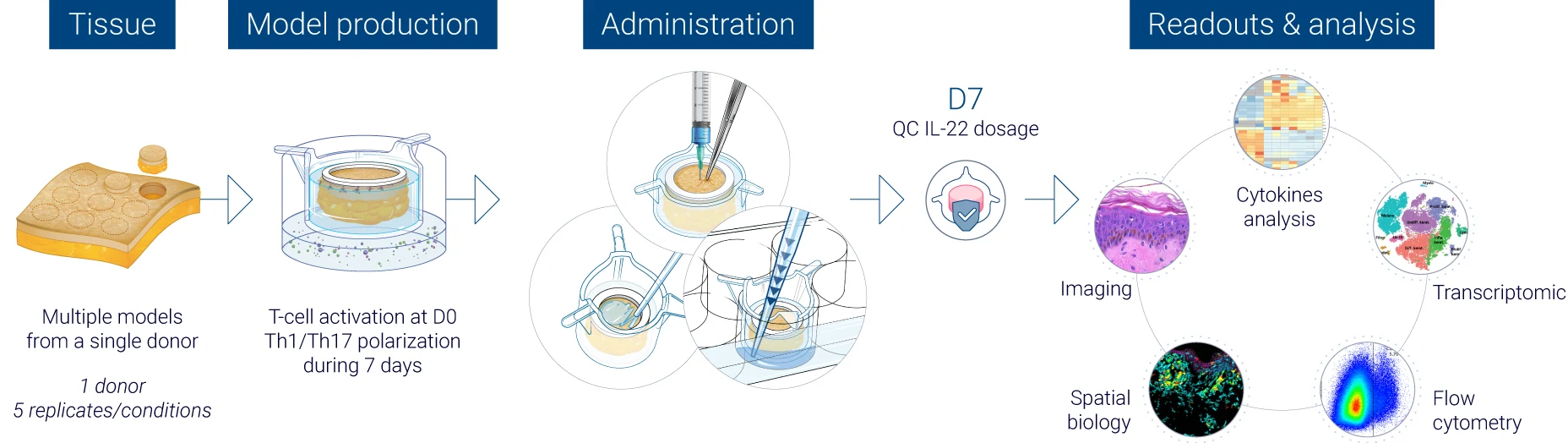
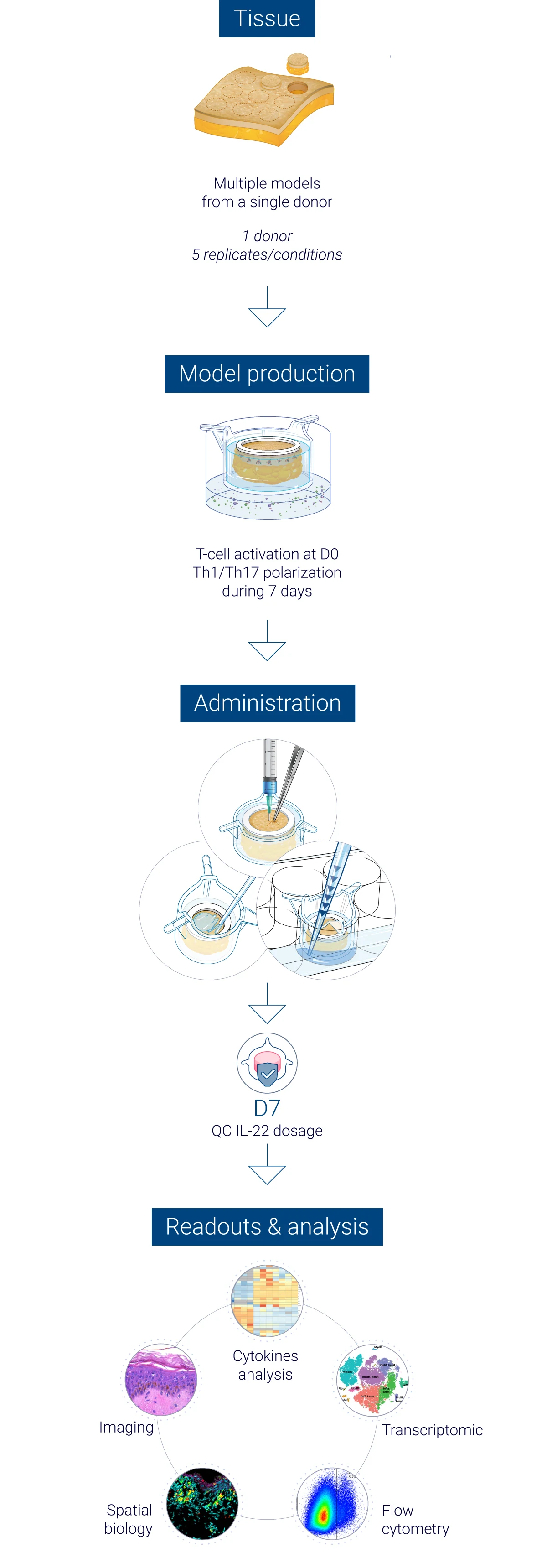
Robust quality control at every stage of the study
From donor selection to analysis: a controlled workflow

The results obtained from our InflammaSkin® data generation platform are analysed by a team of experts in human skin and immunology, who work with cutting-edge tools to help you obtain the results that help your research move forward. Our experts master the traditional, standard tests as well as the latest technology to assess skin inflammation, epidermal activation and tissue integrity. We focus on generating unbiased and accurate human data to support safer and faster drug development. Below you’ll find an illustration of our psoriasis research study process.
Scientific publications using our technology & services
See how others use our Inflammaskin® model and services

July 2024 - Press Release - Scinai Immunotherapeutics announces promising results in an in-vivo proof-of-concept psoriatic human skin model
PR – July 15th, 2024.
The results confirm and build upon previous reported results from ex-vivo studies done with human skin specimens (conducted by Genoskin) and in a plaque psoriasis in vitro model with human skin tissue grown in a dish.
June 2024 - Challenges in psoriasis research: a systematic review of preclinical models.
Published in Karger – June 10, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1159/000538993.
Ana Ubago-Rodríguez, María I. Quiñones-Vico, Manuel Sánchez-Díaz, Raquel Sanabria-de la Torre, Álvaro Sierra-Sánchez, Trinidad Montero-Vílchez, Ana Fernández-González, Salvador Arias-Santiago.
December 2023 - The development of human ex vivo models of inflammatory skin conditions.
Published in National Library of Medicine – December 8, 2023. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec;24(24):17255. doi:10.3390/ijms242417255.
Eddy Hsi Chun Wang, Rebecca Barresi-Thornton, Li-Chi Chen, Maryanne Makredes Senna, I-Chien Liao, Ying Chen, Qian Zheng, Charbel Bouez
December 2023 - Press Release - Scinai announces promising results in a psoriatic human skin model
PR – Dec 12th, 2023
The study, conducted by Genoskin, a pioneering French biotechnology company, aimed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effects of Scinai’s NanoAbs. Genoskin’s proprietary human skin models were induced for expression of plaque psoriasis symptoms to enable ex‑vivo examination of the therapeutic effects of drugs targeting underlying mechanisms in the pathogenesis of plaque psoriasis, particularly the IL-17 family of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This disease-induced skin model reproduces key features of plaque psoriasis tissue morphology as well as the cytokine profile associated with the inflammatory state of plaque psoriasis lesions. Genoskin’s model has been successfully validated as a reliable ex-vivo system for testing drugs aimed at plaque psoriasis.
February 2021 - Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Dipropionate foam inhibits Th17 cytokine secretion and improves epidermal barrier markers in a human Th17 skin inflammation model
- Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Dipropionate Foam Inhibits Th17 Cytokine Secretion and Improves Epidermal Barrier Markers in a Human Th17 Skin Inflammation Model
- Published in Dermatologic Therapy – 2021 Feb;11(1):265-274
- Paola Lovato, Li Jiang, Josephine Hebsgaard, David A Ewald, Hanne Norsgaard
- Published in Dermatologic Therapy – 2021 Feb;11(1):265-274
October 2020 - Development and characterization of a human Th17 driven ex vivo skin inflammation model
- Development and characterization of a human Th17‐driven ex vivo skin inflammation model
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – Oct. 2020;29(10):993-1003.
- Claire Jardet, Anthony David, Emilie Braun, Pascal Descargues, Jean-Louis Grolleau, Josephine Hebsgaard, Hanne Norsgaard, Paola Lovato
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – Oct. 2020;29(10):993-1003.
January 2020 - Translational drug discovery and development with the use of tissue-relevant biomarkers: Towards more physiological relevance and better prediction of clinical efficacy
- Translational drug discovery and development with the use of tissue-relevant biomarkers: Towards more physiological relevance and better prediction of clinical efficacy
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – 2020 Jan;29(1):4-14
- Peter Florian, Klaus R Flechsenhar, Eckart Bartnik, Danping Ding-Pfennigdorff, Matthias Herrmann, Paul J Bryce, Frank O Nestle
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – 2020 Jan;29(1):4-14
October 2019 - Improvements of both inflammation and skin barrier in a human Th17 skin inflammation model by topical treatment with fixed-dose combination calcipotriene/betamethasone dipropionate foam
- Improvements of both inflammation and skin barrier in a human Th17 skin inflammation model by topical treatment with fixed-dose combination calcipotriene/betamethasone dipropionate foam
- Published in Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology – October 01, 2019, Volume 81, Issue 4, Supplement 1, AB79
- Hanne Norsgaard, Paola Lovato, Li Jiang, Josephine Hebsgaard, David Adrian Ewald
- Published in Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology – October 01, 2019, Volume 81, Issue 4, Supplement 1, AB79
September 2019 - Poster - Evaluation of pharmacological responses to subcutaneous injection of adalimumab in InflammaSkin®, a full-thickness human ex vivo skin model reproducing key features of psoriatic lesions
- Evaluation of pharmacological responses to subcutaneous injection of adalimumab in InflammaSkin®, a full-thickness human ex vivo skin model reproducing key features of psoriatic lesions
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
- C. Jardet (Genoskin), E. Bartnik (Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland), D. Ding-Pfennigdorff (Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland), E. Braun (Genoskin), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
May 2018 - Poster - 3D imaging of cleared ex vivo normal human skin, skin appendages and psoriasiform skin lesion using light-sheet microscopy
- 3D imaging of cleared ex vivo normal human skin, skin appendages and psoriasiform skin lesion using light-sheet microscopy
- Scientific Poster presented at the International Investigative Dermatology (IID) 2018 Meeting – 16-19 May 2018
- C. Jardet (Genoskin), S. Abadie (Syntivia), M. Pastore (Genoskin), J. Colombelli (Advanced Digital Microscopy – IRB), B. Chaput (CHU Toulouse Rangueil), A. David (Genoskin), J.-L. Grolleau (CHU Toulouse Rangueil), P. Bedos (Syntivia), V. Lobjois (ITAV), P. Descargues (Genoskin), J. Roquette (ITAV)
- Scientific Poster presented at the International Investigative Dermatology (IID) 2018 Meeting – 16-19 May 2018
September 2017 - Poster - Evaluation of pharmacological responses in a fully human ex vivo skin model following in situ T cell activation with Th17/Th1 psoriasis-like phenotype
- Evaluation of pharmacological responses in a fully human ex vivo skin model following in situ T cell activation with Th17/Th1 psoriasis-like phenotype damage and impairment of protein quality control systems in keratinocytes exposed to a volatile organic compounds cocktail
- Scientific Poster presented at the 47th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 27 to 30, 2017
- P. Lovato (LEO Pharma), C. Jardet (Genoskin), E. Pagès (Genoskin), H. Norsgaard (LEO Pharma), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at the 47th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 27 to 30, 2017