New study model for injectable anti-psoriasis drugs
A hi-tech psoriasis skin model to study drug efficacy
To evaluate the efficacy of injectable anti-psoriasis drugs, the Genoskin team has designed a new test model that combines the InflammaSkin® and HypoSkin® technologies. Below you’ll find a proof-of-concept case study that illustrates the relevance of the new Hypo-InflammaSkin® model during efficacy studies of injectable psoriasis treatments.
Psoriasis & the emerging market of monoclonal antibodies
The global psoriasis treatment market is expected to reach nearly $10 billion by 2024 with an increasing share for psoriasis biologics (1). In order to provide an alternative to topical and oral systemic therapies, the first biologics for the treatment of psoriasis appeared on the market in 2003. Currently, six FDA-approved biologics are available and belong to three drug classes: TNF-α inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors and IL-17 inhibitors. The latest approach consists in specifically targeting both pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-17A and IL-17F (2) to treat the condition.
Testing new subcutaneous psoriasis biologics
A hi-tech psoriasis skin model to increase study efficacy
To evaluate the efficacy of psoriasis biologics, Genoskin has designed an innovative ex vivo human psoriasis model that combines two study models. The InflammaSkin® model (epidermis + dermis) is currently the only ex vivo human T cell-driven psoriasis model with a Th17/Th1 phenotype (3,4). When combined with Genoskin’s HypoSkin® technology (epidermis + dermis + hypodermis), this psoriasis model allows screening and testing biologics that are injected in the adipose tissue. The Hypo-InflammaSkin® model can be used to assess prophylactic treatments for up to 7 days as well as therapeutic treatments for up to 4 days.
Hypo-InflammaSkin® and the Adalimumab psoriasis treatment
A case study using the Hypo-InflammaSkin® model
To test the efficacy of the TNF-α inhibitor Adalimumab, the fully human monoclonal antibody was subcutaneously injected into the fat tissue layer of the Hypo-InflammaSkin® model. The injection occured immediately after model production (prophylactic treatment) or at day 3 post-production (therapeutic treatment). The effect of the anti-psoriasis treatment was evaluated through tissue integrity, expression of specific biomarkers of psoriasis and pro-inflammatory cytokine.
The therapeutic effects of Adalimumab on Hypo-Inflammaskin®
Prophylactic and therapeutic treatments with Adalimumab had positive effects on psoriatic phenotype of Hypo-InflammaSkin®: improvement of epidermis integrity, decrease of S100A7 (psoriasin) and decrease of IL-22 release.
The treatment with subcutaneous injection at day 3 of culture, i.e. when the psoriatic phenotype is established, appeared to be the most efficient. Histological characterization after 7 days of culture showed that the epidermal structure and the viability of the tissue were restored. In addition, a decrease in S100A7 (psoriasin) was observed with Adalimumab .
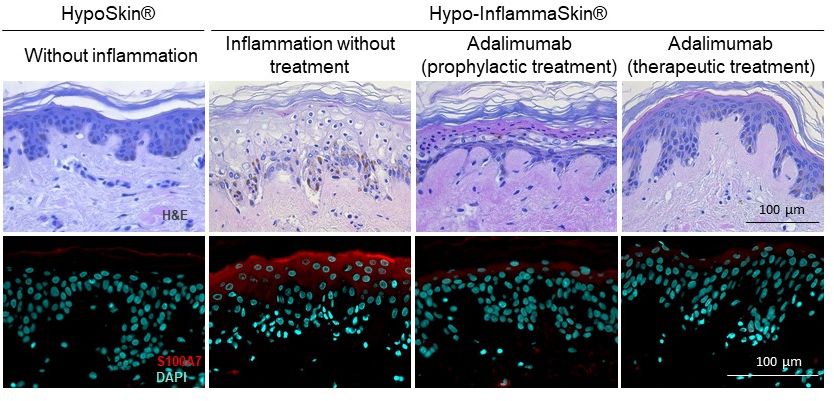
Histological characterization 7 days post-culture following Hypo-InflammaSkin® treatment with Adalimumab
Levels of IL-22 release in the culture medium were also reduced after 7 days of culture following subcutaneous injection of Adalimumab.
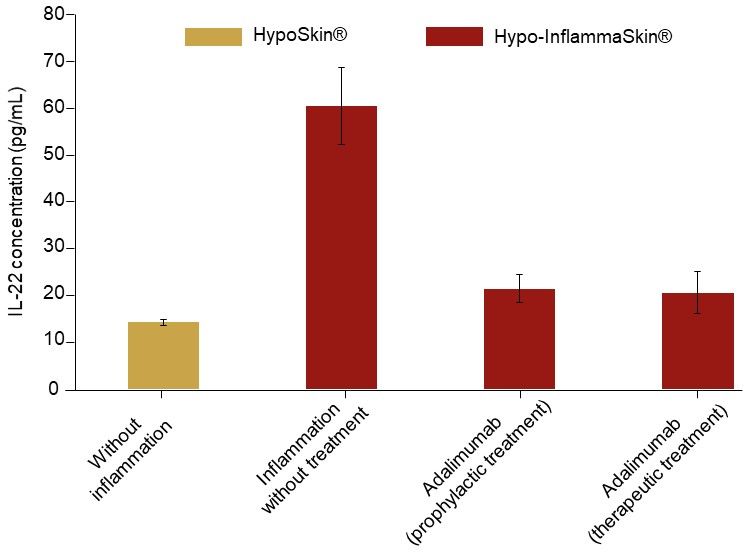
IL-22 release at day 7 of culture following Hypo-InflammaSkin® treatment with Adalimumab
Conclusion
Not only does this case study show the therapeutic effects of subcutaneous injections with Adalimumab, it also illustrates the relevance of Hypo-InflammaSkin® as a skin model to test drugs for efficacy on psoriatic lesions.
For more information on the HypoSkin® study model for subcutaneous injections, don’t hesitate to visit our website. The InflammaSkin® and Hypo-InflammaSkin® models are currently part of our in-house services, which are tailored to your needs and requirements. Should you already have an anti-psoriasis drug you’d like to test out, don’t hesitate to contact us.
References
(1) Decision Resources Group (2016). Biologics continue to flare up the psoriasis market, indicating opportunities in the larger dermatology space. Available at: https://decisionresourcesgroup.com/drg-blog/biologics-continue-flare-psoriasis-market-indicating-opportunities-larger-dermatology-space/ (2) Mylle et al. (2018). Targeting the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in psoriasis: the search for the good, the bad and the ugly. Am J Clin Dermatol. (3) Lovato et al. (2017). Evaluation of pharmacological responses in a fully human ex vivo skin model following in situ T cell activation with Th17/Th1 psoriasis-like phenotype. J Invest Dermatol. 137(10S):S210. (4) Lovato et al. (2018). Evaluation of pharmacological responses in InflammaSkin® a fully human full-thickness ex vivo skin model reproducing key features of psoriatic lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 138(5S):S168.
Comments are closed.