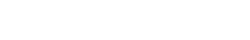Human Primary Mast Cells
Evaluate in vitro mast cell response
Human primary mast cells for research
Reliable human data on drug efficacy & toxicity

Today’s research on new drugs is often complicated by a consistent lack of relevant study tools. This is also the case when it comes to research on mast cells, where rodent and human cell line models are still the standard and human primary mast cells remain notoriously hard to obtain. Genoskin provides a reliable solution to help you study human primary mast cell response to your compound or formula. You’ll find a quick overview of our offer below.
Toxicity assessment
Monitor mast cell degranulation to evaluate potential drug toxicity and identify adverse effects mediated by mast cells.
Allergic reactions
Analyze a drug candidate effects on mast cells degranulation to help assess its potential for inducing allergic responses in patients.
Drug efficacy
Assess the efficacy of a drug candidate in inducing mast cell degranulation as an indicator of the desire immune response.
Ready to test in vitro-derived mast cells in your lab?
Unlock new research potential with our reliable human primary mast cells—now available for your experiments!

Genoskin is excited to offer Human Peripheral Blood-derived Mast Cells (PBCMCs) as a product, empowering you to conduct cutting-edge research directly in your own lab. These mast cells, which are cultured from peripheral blood CD34+ progenitor cells, are, integral to immune responses, are essential for research on allergic reactions, immune system responses, and a range of pathologies. Genoskin’s functional human primary mast cells are designed for in vitro research on drug efficacy, toxicity, and immune responses, with reliable degranulation in response to anti-IgE stimulation.
Ready to enhance your research? Our mast cells are waiting for you. Now, you can take full control of your experiments with these powerful cells, all at your fingertips—ready to be used in your lab at your convenience. Please note that mast cells are only available for delivery in Europe and the United Kingdom.
Human primary mast cells
Key players in immunology
Mast cells play an important role in how the immune system responds to certain bacteria and parasites and they also help control other types of immune responses. They have been mostly viewed as effectors of allergy and it has only been in the last two decades that they have gained significant attention for their involvement in a range of other physiological and pathological processes. Mast cells are a type of white blood cell found in connective tissues throughout the human body. Investigations have shown that they are present in the skin and in nearly all vascularized organs, including heart, lungs, kidneys, intestine, liver and in the brain side of the blood-brain barrier. They contain chemicals such as histamine, heparin, cytokines, and growth factors, which they release during allergic reactions and certain immune responses (Sarit Pal et al., 2020).
First-in-human data on drug efficacy and toxicity
A unique platform to de-risk drug development

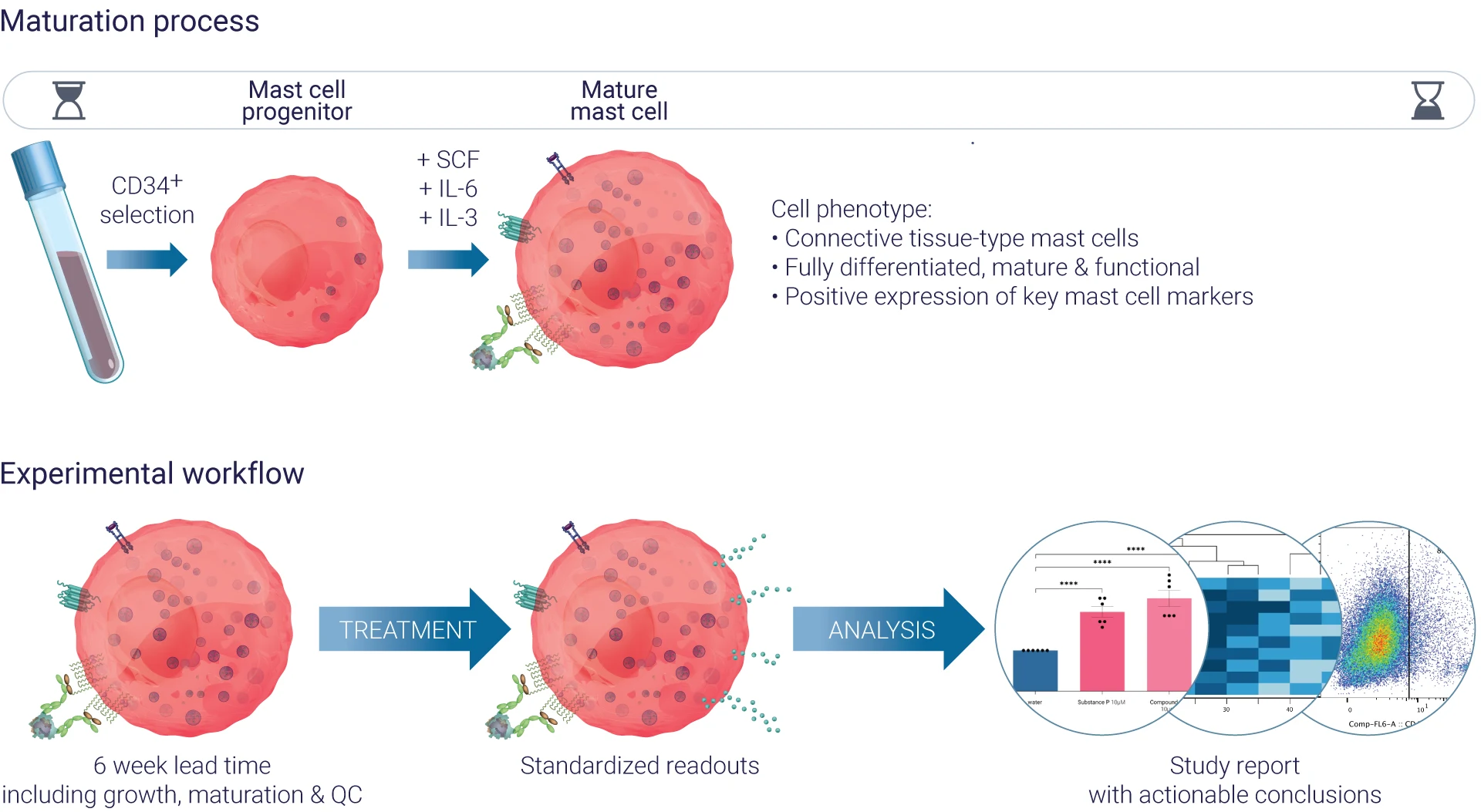
As human primary mast cells are notoriously hard to obtain for research purposes, Genoskin has developed a unique process using peripheral blood samples from healthy adult donors. This 1-month process yields mature mast cells that show the same metabolism and expression as the mast cells in the human body, with the phenotype of connective tissue-type mast cells:
- The granules are filed with heparin, tryptase and chymase
- They express the high affinity receptor for IgE (FcεR1α), MRGPRX2 (specifically expressed by skin mast cells), FcgRs and many G protein-coupled receptors including receptors for complement anaphylatoxins
- They can degranulate and produce cytokines/chemokines in response to many stimuli including IgE/anti-IgE, cationic molecules that bind to MRGPRX2 (e.g neuropeptide substance P and FDA-approved drugs), C3a and C5a, endothelin-1,…
Mature human mast cells express a diverse array of surface receptors that enable them to detect and respond to a multitude of signals, ranging from antibodies and complement components to cytokines, neuropeptides, and microbial products. This receptor repertoire allows mast cells to play pivotal roles in both protective immune responses and pathological conditions such as allergies, asthma, and autoimmune diseases. We tested the expression of three key receptors in our in vitro cultured mature human mast cells using flow cytometric analysis.
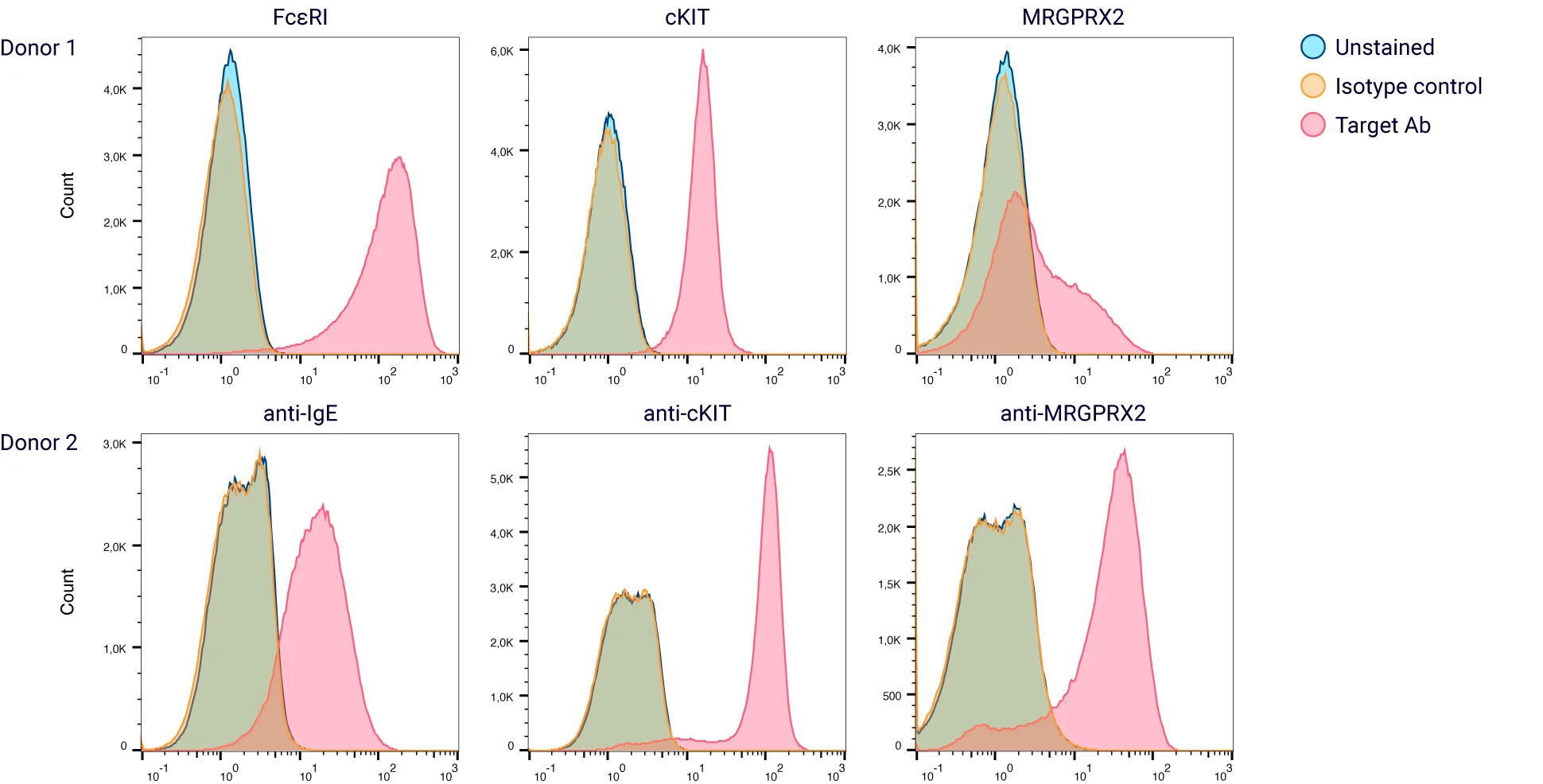
The majority of in vitro differentiated cell co-express cKIT and FcεR1α; the expression of MRGPRX2 is variable between donors
Fully mature & functional mast cells
Genoskin’s mature connective-tissue type mast cells (CTMCs) are fully differentiated. Their heparin-filled granules can be specifically stained with Avidin, similar to what is observed with CTMCs in the skin. As shown in the graphs below, FcεR1α & MRGPRX2 are functional and display normal activity upon stimulation. To obtain these results, ß-hexosaminidase activity was measured in the culture supernatant.
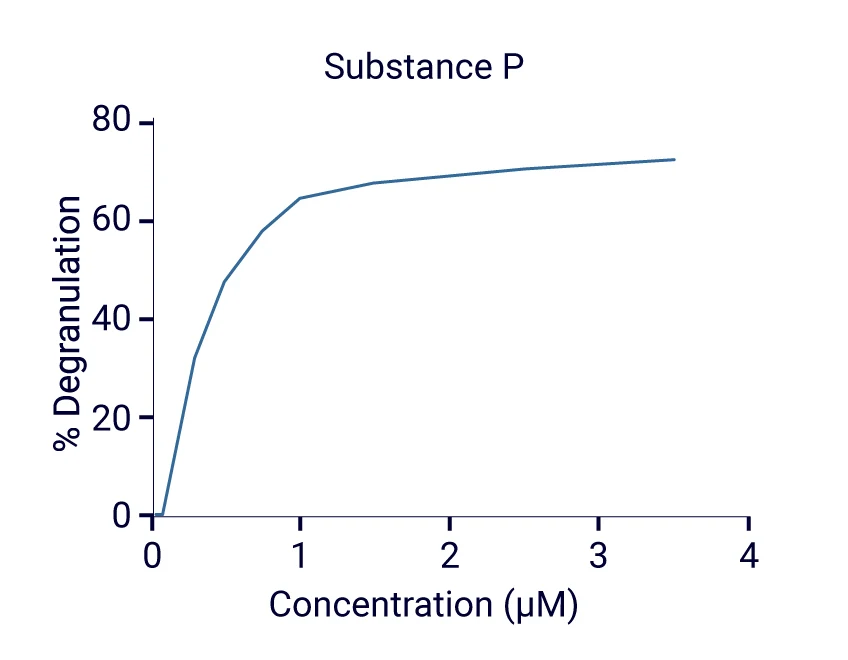
Upon stimulation of the receptor MRGPX2 with Substance P, ß-hexosaminidase activity was detected in the culture supernatant (50k cells/well)
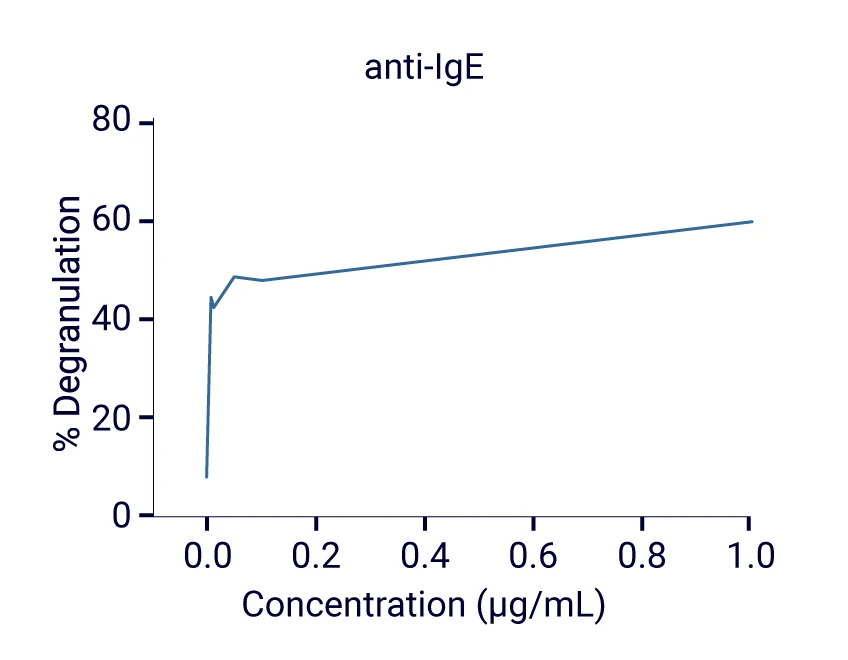
Upon stimulation of the Fcɛ receptor 1⍺ with an IgE agonist antibody, ß-hexosaminidase activity was detected in the culture supernatant (50k cells/well)
CD63 Staining via Flow Cytometry: A Powerful Tool for Mast Cell Degranulation Studies
Genoskin expands its non-clinical testing services with the introduction of CD63 staining via flow cytometry. This advanced method enhances the measurement of mast cell degranulation studies by precisely measuring CD63 surface expression at the single-cell level. Ideal for drug development, safety assessments, and immune research, CD63 staining allows for high-sensitivity detection of degranulation and can be paired with other markers for multi-parameter analysis.
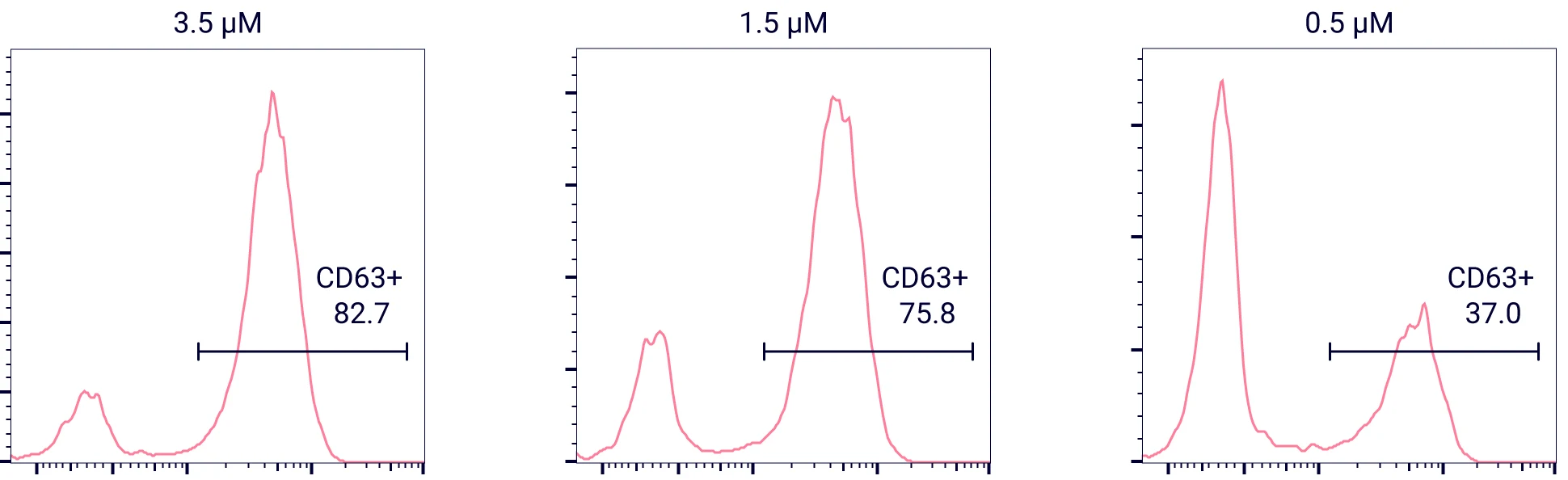
Substance P activation
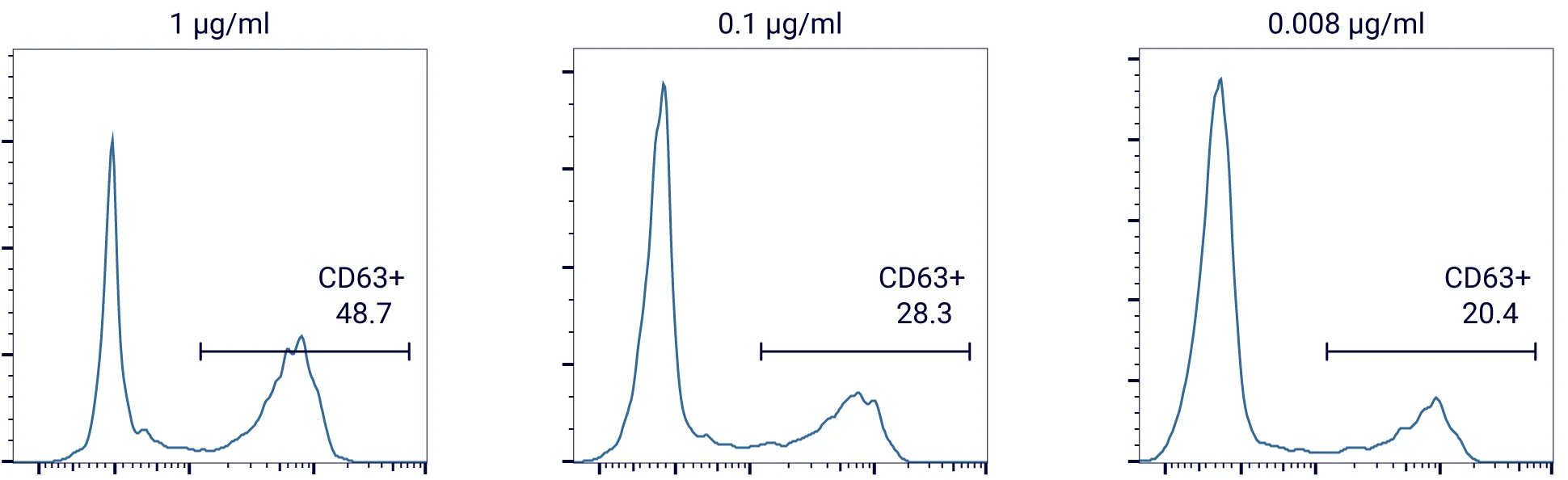
Anti-IgE activation
Resources

September 2016 - Different activation signals induce distinct mast cell degranulation strategies
- Different activation signals induce distinct mast cell degranulation strategies
- Published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation – September 19, 2016
- Nicolas Gaudenzio, Riccardo Sibilano, Thomas Marichal, Philipp Starkl, Laurent L. Reber, Nicolas Cenac, Benjamin D. McNeil, Xinzhong Dong, Joseph D. Hernandez, Ronit Sagi-Eisenberg, Ilan Hammel, Axel Roers, Salvatore Valitutti, Mindy Tsai, Eric Espinosa, and Stephen J. Galli.
- Published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation – September 19, 2016
March 2013 - Human mast cells drive memory CD4+ T cells toward an inflammatory IL-22+ phenotype
- Human mast cells drive memory CD4+ T cells toward an inflammatory IL-22+ phenotype
- Published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology – March 20,2013
- Nicolas Gaudenzio, PhD, Camille Laurent, MD, Salvatore Valitutti, MD, Eric Espinosa, PhD
- Published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology – March 20,2013
Mast cells factsheet
Webinar – Mast Cells: Can’t live with them, can’t live without them?
April 8, 2024 – Prof. Marcus Maurer
In this webinar, Prof. Maurer focuses on the dual role of mast cells in health and inflammatory diseases.
Webinar – MRGPRX2+ Mast Cells : From Biology to Clinical Perspective in Skin Immunology
May 2024 - Poster - Single-cell Profiling of Biostabilized Natural Human Skin Identifies Mast Cells as an Important Target of Injected mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine
- Single-cell Profiling of Biostabilized Natural Human Skin Identifies Mast Cells as an Important Target of Injected mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine
- Scientific poster presented at the European Mast cell and Basophil Research Network (EMBRN) conference in – Mai 2024
- Manon Scholaert, Mathias Peries, Emilie Braun, Jeremy Martin, Nadine Serhan, Katarzyna Polak, Alexia Loste, Audrey Bruner, Lilian Basso, Benoit Chaput, Eric Merle, Pascal Descargues, Emeline Pagès, Nicolas Gaudenzio
- Scientific poster presented at the European Mast cell and Basophil Research Network (EMBRN) conference in – Mai 2024