Hyposkin® human skin models
Live immune response to subcutaneous injection
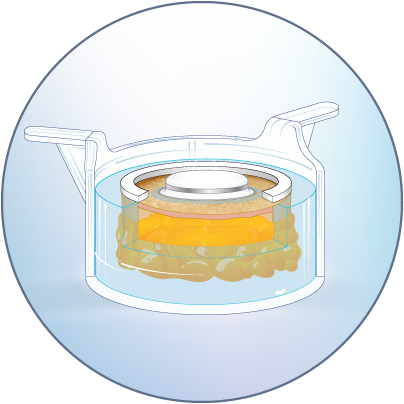
The HypoSkin® live human skin model
First-in-human data generation for subcutaneous injections

HypoSkin® human skin models currently offer the closest alternative to directly injecting a compound in an actual person’s skin. They are designed to help drug and vaccine developers accelerate the selection of viable drug candidates. Thanks to a unique technology, our models facilitate the acquisition of relevant and accurate first-in-human data when it comes to injection site reactions, immunology or metabolism. Here is an overview of the HypoSkin® benefits:
Immunocompetent
HypoSkin® models have the features and functionalities of in vivo human skin, with all skin and immune cells, to generate predictive human data.
Standardized
Model generation is standardized to ensure reproducible testing on real, live human epidermis, dermis and adipose tissue
Injection
The HypoSkin® model is the only human skin model on the market to study live response to subcutaneous and intradermal injections.
Platform
HypoSkin® is suitable for a broad range of applications, from injection site reactions over medical devices to studying bolus injections.
Human immune response to your drug
A full week of testing opportunities
Due to the current lack of research tools to study response to injections in humans, the development of injectable therapeutics remains challenging, with animal testing as the only option. Genoskin’s HypoSkin® model is the first human skin study platform in the world that allows subcutaneous and intradermal injection in humans without harming either humans or animals. HypoSkin® models provide crucial information on the response of real, live human skin and immune cells to drugs, vaccines and medical devices. The skin is bio-stabilized thanks to our patented technology, which allows keeping real human skin alive for 7 days. This approach helps us provide a highly relevant and reliable solution to pharmaceutical, biotech, cosmetic and chemical companies to test their compounds on and in real human skin for an entire week.
The HypoSkin® project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 816289 (SME Instrument).
Study human immune cell response to derisk drug development
Live human immune cells in their native environment

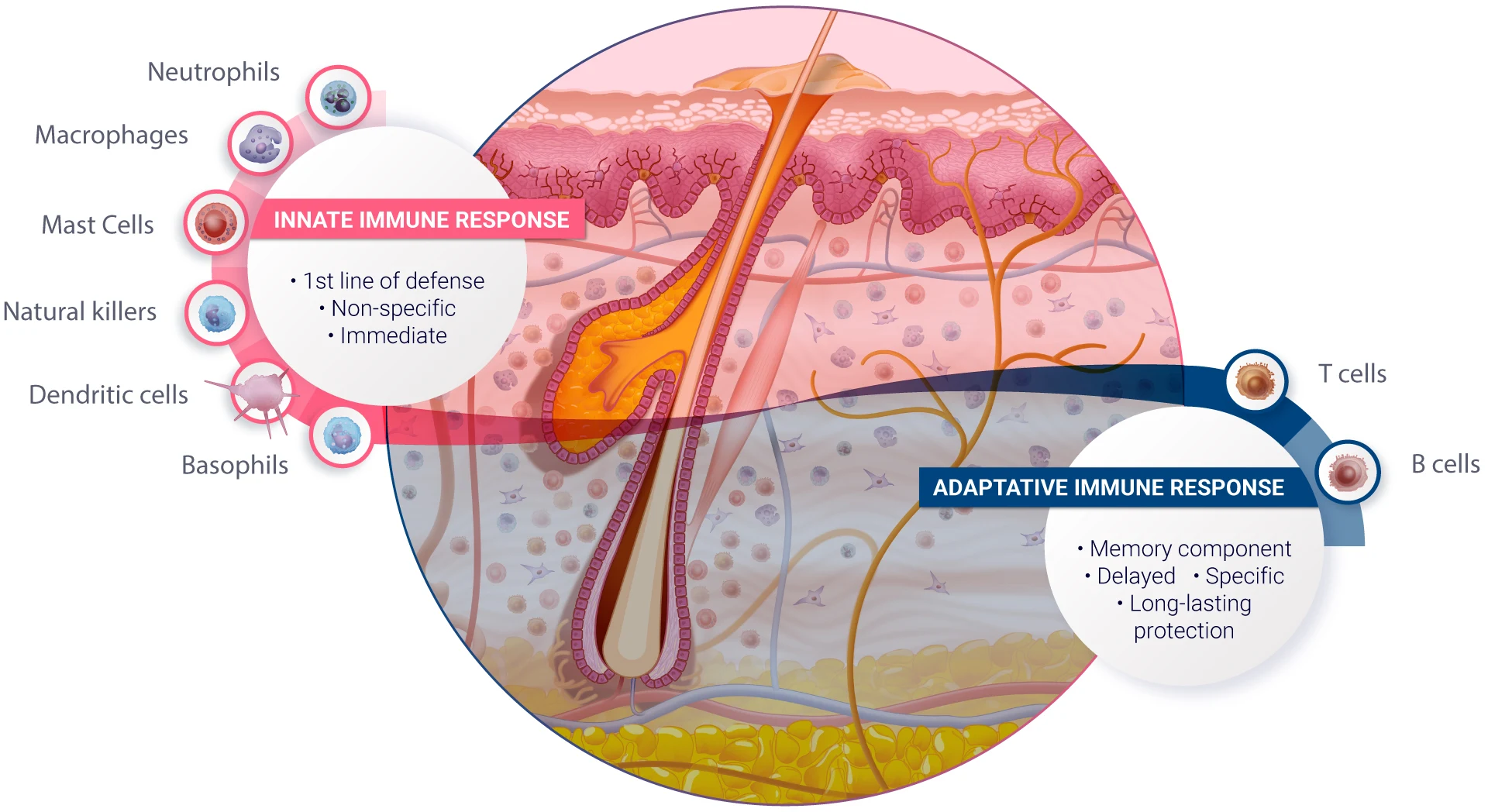
Human skin provides an exceptional model for studying the responses of structural cells, such as melanocytes, keratinocytes, and sebaceous glands, to various formulations. Real human skin also possesses an extraordinary diversity of immune cells that are involved in drug-induced immunotoxicity (Tokura et al., 2021 & Kabashima et al., 2019). The immune cells we find in the skin (resident memory CD4 and CD8 T lymphocytes, dendritic cell subsets, innate lymphoid cells, natural killer cells, macrophages, mast cells, some B cells and others… ) are also present in other human organs (Nguyen et al., 2019). In real skin, immune and structural cells constantly interact together to form a true ecosystem, which is key to apprehending human immunological response to drugs and formulations prior to clinical trials.
HypoSkin®, a flexible study platform for first-in-human data
Explore a variety of administration routes
The HypoSkin® model is composed of live human epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. It is the first model on the market that allows for research on subcutaneous injection in human skin. It is also suitable for studies of different types of biologics and small molecule drugs using the other routes of administration such as:
Transdermal application
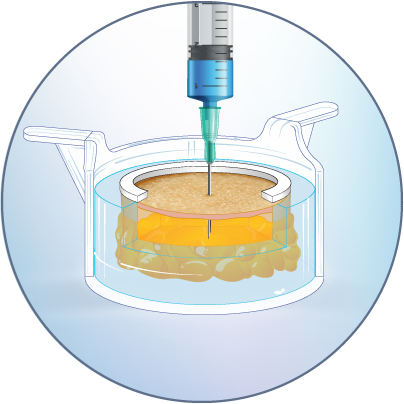
ID or SQ injection or insertion
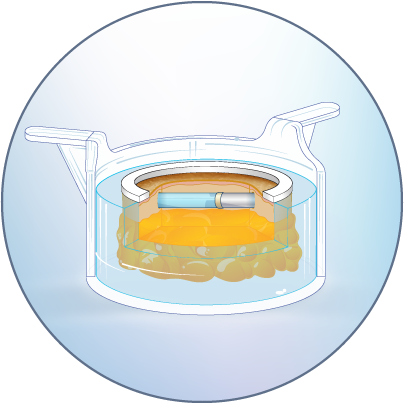
Infusion
A wide range of applications
Explore all the possibilities of immunocompetent and injectable human skin

The HypoSkin® model is suitable for a wide range of applications, including first-in-human efficacy and toxicity studies, prior to clinical trials. The model allows for in-depth immunological studies that can provide a window to the immune response of the human body after drug or vaccine administration. Below, you’ll find some examples of the types of studies you can conduct with the HypoSkin® model.
Bolus injection
Medical device testing
Dermal filler characterization
Scientific publications using HypoSkin®
See how others use the HypoSkin® model to generate results

August 2022 - Immortalized human myoblast cell lines for the delivery of therapeutic proteins using encapsulated cell technology
- Immortalized human myoblast cell lines for the delivery of therapeutic proteins using encapsulated cell technology
- Published in Molecular Therapy Methods & Clinical Development – VOLUME 26, P441-458, SEPTEMBER 08, 2022
- Aurelien Lathuiliere, Remi Vernet, Emily Charrier, Muriel Urwyler, Olivier Von Rohr, Marie-Claude Belkouch, Valentin Saingier, Thomas Bouvarel, Davy Guillarme, Adrien Engel, Patrick Salmon, Thomas Laumonier, Julien Grogg, Nicolas Mach
- Published in Molecular Therapy Methods & Clinical Development – VOLUME 26, P441-458, SEPTEMBER 08, 2022
November 2021 - A suspended layer additive manufacturing approach to the bioprinting of tri-layered skin equivalents
- A suspended layer additive manufacturing approach to the bioprinting of tri-layered skin equivalents
- Published in APL Bioengineering – 2021 Nov 30;5(4):046103.
- Richard J A Moakes, Jessica J Senior, Thomas E Robinson, Miruna Chipara, Aleksandar Atansov, Amy Naylor, Anthony D Metcalfe, Alan M Smith, Liam M Grover
- Published in APL Bioengineering – 2021 Nov 30;5(4):046103.
July 2021 - Poster - Mitigation of Injection Site Reactions after Subcutaneous Administration of Dalcinonacog Alfa (DalcA) in Hemophilia B Using Preclinical Models
- Mitigation of Injection Site Reactions after Subcutaneous Administration of Dalcinonacog Alfa (DalcA) in Hemophilia B Using Preclinical Models
- Scientific Poster – ISTH 2021 Congress – Abstract PB0453
- N. Le Moan, L. Kelly, E. Merle, P. Descargues, N. Gaudenzio, H. Gagnon, A. Chatterji, G.E. Blouse
- Scientific Poster – ISTH 2021 Congress – Abstract PB0453
July 2021 - Poster - Assessing subcutaneous injection site reactions by leveraging immunocompetent human skin and artificial intelligence
- Assessing subcutaneous injection site reactions by leveraging immunocompetent human skin and artificial intelligence
- Scientific Poster – CRS 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting – July 25 to 29, 2021.
- Emeline Pagès, Emilie Braun, Eric Merle, Pascal Descargues, Nicolas Gaudenzio
- Scientific Poster – CRS 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting – July 25 to 29, 2021.
December 2020 - Standalone or combinatorial phenylbutyrate therapy shows excellent antiviral activity and mimics CREB3 silencing
- Standalone or combinatorial phenylbutyrate therapy shows excellent antiviral activity and mimics CREB3 silencing
- Published in Science Advances – 2020 Dec 4;6(49):eabd9443
- Tejabhiram Yadavalli, Rahul Suryawanshi, Raghuram Koganti, James Hopkins, Joshua Ames, Lulia Koujah, Aqsa Iqbal, Krishnaraju Madavaraju, Alex Agelidis, Deepak Shukla
- Published in Science Advances – 2020 Dec 4;6(49):eabd9443
August 2019 - Near-infrared light activable hydrogels for metformin delivery
- Near-infrared light activable hydrogels for metformin delivery
- Published in Nanoscale – 2019 Aug 29;11(34):15810-15820
- Li Chengnan, Quentin Pagneux, Anna Voronova, Alexandre Barras, Amar Abderrahmani, Valérie Plaisance, Valerie Pawlowski, Nathalie Hennuyer, Bart Staels, Lea Rosselle, Nadia Skandrani, Musen Li, Rabah Boukherroub, Sabine Szunerits
- Published in Nanoscale – 2019 Aug 29;11(34):15810-15820
December 2018 - Poster - A fully functional ex vivo human skin model to study human skin microbiome
- A fully functional ex vivo human skin model to study human skin microbiome
- Scientific Poster presented at the BacTouBac meeting of the Paul Sabatier University in Toulouse – December 11 & 12, 2018
- B. Coupe (Vaiomer), M. Pastore (Genoskin), E. Pagès (Genoskin), E. Braun (Genoskin), A. Broha (Vaiomer), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at the BacTouBac meeting of the Paul Sabatier University in Toulouse – December 11 & 12, 2018
January 2018 - Poster - Evaluation of local inflammatory reactions following subcutaneous injection of a pro-inflammatory cocktail in a fully human ex vivo skin model
- Evaluation of local inflammatory reactions following subcutaneous injection of a pro-inflammatory cocktail in a fully human ex vivo skin model
- Scientific Poster presented at DECHEMA Advances in Medical Biology Seminar – January 30 to 31, 2018
- C. Jardet (Genoskin), E. Pagès (Genoskin), E. Raude (Genoskin), F. Seeliger (AstraZeneca), L. Brandén (AstraZeneca), E. Braun (Genoskin), M. Ingelsten (LAAS-CNRS), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at DECHEMA Advances in Medical Biology Seminar – January 30 to 31, 2018